Research design
Because the CALLIDUS-project aims to be a collaboration of university and different schools the design-based research approach has been choosen for this interdisciplinary project.
Design-based Research
„Design Research is not defined by methodology. All sorts of methods may be employed. What defines design research is its purpose: sustained innovative development.” (Bereiter 2002, 330)
The CALLIDUS-project combines applied sciences (corpus-based tasks for teaching Latin) and basic research (corpus-based methods for language acquisition). Therefore the approach of design-based research (DBR) is used to evaluate the studies and the software.
„In summary, design experiments are extended (iterative), interventionist (innovative and design-based), and theory-oriented enterprises whose “theories” do real work in practical educational contexts.” (Cobb et al. 2003, 13)
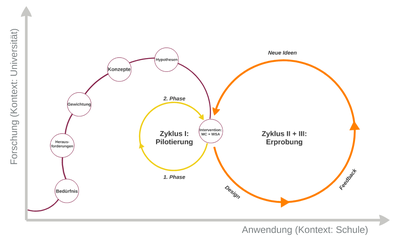
The phases of design-based research
Phase 1: Exploration and analysis of the context
In the first phase the real teaching and learning context (practice) as well as the literature (theory) were analysed. Topics were the following:
- Vocabulary acquisition (in general and for teaching Latin)
- Testing effect, types of (corpus-based) tests
- Types of linguistic exercises and tasks
- Digital learning: mobile learning, blended learning, flipped classroom; learning analytics, educational data mining; Moodle
- Linguistic and cognitive insights about the mental lexicon, procedures of vocabulary learning, connectionist theories, theory of mind, ...
- Corpuslinguistics: analyses of frequency and association, POS-Tagging, stemming, treebanking, domain specific languages (AQL)
- Software engineering: user friendly GUI, formats of data, frameworks, desktop vs. app, ...
- Study concept: beginners vs. intermediate learners, selection of texts, development of teacher-friendly teaching material, ...
On the basis of this first phase the main and design principles of the intervention were deduced.
Phase 2: Design of the intervention
The intervention includes two aspects: Giving the teachers corpus-based vocabulary acquisition material (paper) and developing a software which uses corpus-based techniques to create vocabulary learning exercises. Thus, both parts form the whole intervention.
Phase 3: Evaluation
- Test of the (analog) materials with pre- and posttests and feedback of the teachers
- Test of the software with feedback of users and statistics
Literature:
-
Anderson, T.; Shattuck, J. (2012): Design-Based Research: A Decade of Progress in Education Research? In: Educational Researcher 41 (1), 16–25.
-
Jahn, D. (2014): Durch das praktische Gestalten von didaktischen Designs nützliche Erkenntnisse gewinnen: Eine Einführung in die Gestaltungsforschung. In: Wirtschaft und Erziehung 66 (1), S. 3–15.
-
McKenney, S.; Reeves, T. C. (2013): Systematic Review of Design-Based Research Progress: Is a Little Knowledge a Dangerous Thing? In: Educational Researcher 42 (2), S. 97–100.
-
McKenney, S.; Reeves, T. (2012): Conducting educational design research. New York: Routledge.
-
Reinmann, G. (2005): Innovation ohne Forschung? Ein Plädoyer für den Design-Based Research-Ansatz in der Lehr-Lernforschung. in: Unterrichtswissenschaft 33 (2005) 1, 52-69.